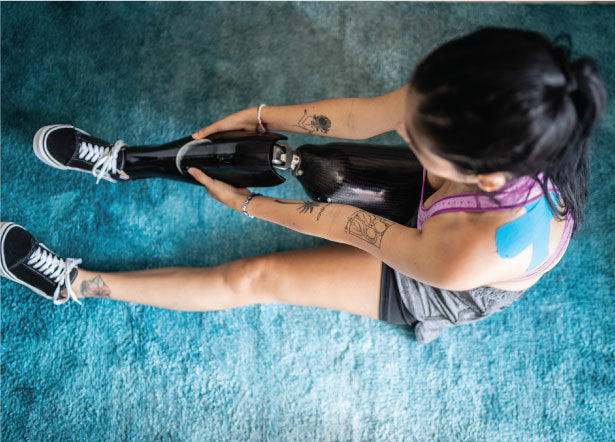
What are common prosthetic parts of an AK prosthesis?
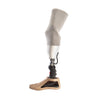
In individuals with transfemoral amputations, a quadrilateral or an ischial containment socket is often used. The ischium is another term for the bones of the pelvis that we sit on. In an ischial containment socket, there is better contact between the residual limb and the prosthesis because the ischium is held within the socket together with the residual limb. This allows a better distribution of the weight from the body onto the lower limb as well as providing better stability and muscle function. The quadrilateral socket is named because it has four sides making up its walls. Each wall has certain advantages that enable a transfemoral amputee to walk more effectively and comfortably. It is variable which type of individual with an above-knee amputation uses which type of socket.
Various suspension systems that keep the prosthesis held onto the residual limb are available. One type of suspension system uses one of two types of belts either known as a Silesian belt or Total Elastic Suspension (TES) belt. The Silesian belt anchors to the socket on its outer aspect and then wraps around the person’s pelvis, opposite hip and then reattaches back to the anterior socket. The TES belt is different than the Silesian belt. It is made from elastic neoprene and is worn around the waist. Because of its ability to retain body heat, it can be quite warm in hotter climates or during the summer months. Fortunately, both of these suspension devices can be adjusted in size for comfort.
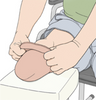
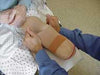
A different type of suspension is referred to as a suction suspension system. There are basically two types of these suction devices, the first being the traditional suction suspension. With this type of suspension the residual limb is pulled into the socket using a donning sock. The donning sock is then pulled out through a valve hole leaving the residual limb snugly in the socket. After the valve hole is sealed, a negative pressure system is created and the limb is held into the prosthesis via a vacuum phenomena. With this system, there is better contact with the prosthesis and less motion that occurs while the limb is in the socket. Excessive motion can be uncomfortable and lead to skin breakdown and blisters, which are obviously not good things particularly if the individual has PVD.
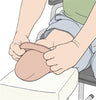
If the person does not have the strength or dexterity to pull the sock through the valve hole, another type of suction device known as roll-on silicon suction suspension can be tried. This type of suction system uses a silicon sleeve rolled onto the residual limb. The outer portion of the silicon sleeve is lubricated and placed into the socket. Once all of the air is displaced out of the socket, the valve hole is then covered, maintaining suspension via a vacuum system. The disadvantage of this system is that the silicon can be hot and the residual limb can become sweaty. Additionally, the residual limb must be of a consistent size and not be swollen. This can be a problem in people who have heart failure or who have kidney failure and require dialysis as these medical problems cause the limbs to fluctuate in size. These suction systems can also be used in conjunction with some of the belt systems described above for added security.
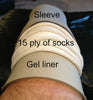
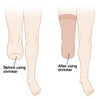
If an individual does have fluctuations in the size of their residual limb, there may be times when the limb may not fit adequately into the socket and the prosthesis will need to be replaced. However, one way to prolong the fit of the socket on a changing limb is to use a flexible socket made of plastic material that can be heated and remolded so as to improve fit. Additionally, slip sockets may be used. A slip socket has one or more thin inner layers or liners that can be peeled out of the socket to accommodate the expanding limb. An individual may also use socks to help improve the fit and longevity of a socket. These socks are made of a thin cloth material that can come in different plies (thicknesses) and when the residual limb changes, the sock ply can be adjusted allowing better fit of the residual limb in the socket.